
Apr 6, 2020
CARES Act: Provisions for Individuals
With much of the country in self-isolation, perhaps you’ve got time to read the entire H.R. 748 Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, or CARES Act. If you’d prefer, here is a summary of many of the key provisions we expect to be discussing with you in person or virtually. We look forward to helping you navigate the nuances of these changes and the direct application to your specific situation.
In General
- Direct payments/recovery rebates: Most Americans can expect to receive rebates from Uncle Sam. Depending on your household income, expect up to $1,200 per adult and $500 per dependent child. To calculate your payment, the Federal government will look at your 2019 Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) if it’s available, or your 2018 AGI if it’s not. However, you’ll receive an extra 2020 tax credit if your 2020 AGI ends up lower than the figure used to calculate your rebate. This Nerd’s Eye View illustration offers a great overview:
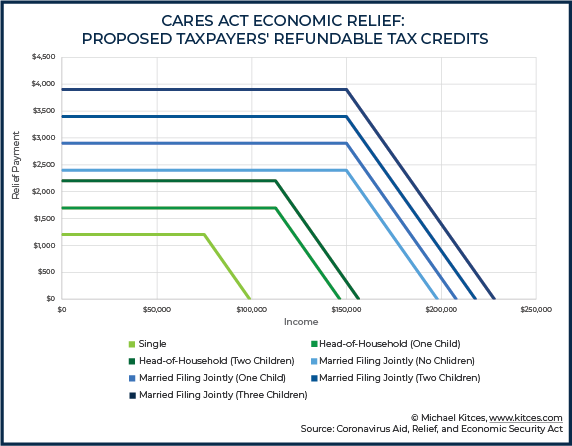
From Michael Kitces at Nerd’s Eye View; reprinted with permission.
- Retirement account distributions for coronavirus-related needs: You can tap into your retirement account ahead of time in 2020 for a coronavirus-related distribution of up to $100,000, without incurring the usual 10% penalty or mandatory 20% Federal withholding. You’ll still owe income tax on the distributions, but you can prorate the payment across 3 years. You also can repay distributions to your account within 3 years to avoid paying income taxes, or to claim a refund on taxes paid.
- Various healthcare-related incentives: For example, certain over-the-counter medical expenses previously disallowed under some healthcare plans now qualify for coverage. Also, Medicare restrictions have been relaxed for covering telehealth and other services (such as COVID-19 vaccinations, once they’re available). Other details apply.
For Retirees (and Retirement Account Beneficiaries)
- RMD relief: Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) go on a holiday in 2020 for retirees, as well as beneficiaries with inherited retirement accounts.
For Charitable Donors
- “Above-the-line” charitable deductions: Deduct up to $300 in 2020 qualified charitable contributions (excluding Donor Advised Funds), even if you are taking a standard deduction.
- Donate all of your 2020 AGI: You can effectively eliminate 2020 taxes owed, and then some, by donating up to, or beyond your AGI. If you donate more than your AGI, you can carry forward the excess up to 5 years. Donor Advised Fund contributions are excluded.
For Unemployed/Laid Off Americans
- Increased unemployment compensation: Federal funding increases standard unemployment compensation by $600/week, and coverage is extended 13 weeks.
- Federal funding covers first week of unemployment: The one-week waiting period to start collecting benefits is waived.
- Pandemic unemployment assistance: Unemployment coverage is extended to self-employed individuals for up to 39 weeks. Plus, the Act offers incentives for states to establish “short-time compensation programs” for semi-employed individuals.
For Students
- Student loan payments deferred to Sept. 30, 2020: No interest will accrue either. Important: Voluntary payments will continue unless you explicitly pause them. Plus, the deferral period will still count toward any loan forgiveness program you’re in. So, be sure to pause payments if this applies to you, lest you pay on debt that will ultimately be forgiven.
- Delinquent debt collection suspended through Sept. 30, 2020: Including wage, tax refund, and other Federal benefit garnishments.
- Employer-paid student loan repayments excluded from 2020 income: From the date of the CARES Act enactment through year-end, your employer can pay up to $5,250 toward your student debt or your current education without it counting as taxable income to you.
- Pell Grant relief: There are several clauses that ease Pell Grant limits, while not eliminating them. It would be best if we go over these with you in person if they may apply to you.
For Estates/Beneficiaries
- A break for “non-designated” beneficiaries: 2020 can be ignored when applying the 5-year rule for “non-designated” beneficiaries with inherited retirement accounts. The 5-Year Rule effectively ends up becoming a 6-Year Rule for current non-designated beneficiaries.
Given the complexities involved and unprecedented current conditions, there will undoubtedly be updates, clarifications, additions, system glitches, and other adjustments to these summary points. Please consult with us and other appropriate professionals, such as your accountant, and/or estate planning attorney on any details specific to you. Please don’t hesitate to reach out to us with your questions and comments. It’s what we’re here for.
Reference Materials:
- DWC News Update, The CARES Act: Federal Coronavirus Relief. March 30, 2020.
- Financial Planning, “Major changes in RMDs and retirement contributions in $2T stimulus plan,” Ed Slott, March 27, 2020.
- H2R CPA, “Cares Act will provide billions of dollars of relief,” March 27, 2020.
- R. 748: Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act.
- Nerd’s Eye View, “Analyzing The CARES Act: From Rebate Checks To Small Business Relief For The Coronavirus Pandemic,” Jeffrey Levine, March 27, 2020.
- The Wall Street Journal, “How the Coronavirus Paid Leave Rules Apply to You,” Charity L. Scott, March 27, 2020.
- ThinkAdvisor, “3 Stimulus Bill Provisions Advisors Should Act On Now: Jeff Levine,” Jeff Berman, March 30, 2020.
